单细胞免疫组库测序一次实验可以同时检测近万个细胞,可在一个样本中同时获5'端mRNA表达谱、TCR和BCR的信息,结合基因的表达谱和V(D)J数据进行复杂组织样本的影响免疫应答分析,监测免疫疗法的效果,研究疾病发生和发展的分子机制。
(图片来源:Wang Y, et al., Journal of Infection, 2023)
1. 1000+ TCR/BCR项目经验,一次实验可同时获取1000-10000个细胞的文库构建,获得转录组和免疫组数据。
2. 具备完善的免疫组库测序和实验质控流程,获取V(D)J全长序列的配对信息。
3. 丰富的免疫组库测序和数据分析经验,实现专属个性化数据分析服务,搭配单细胞分析云平台,一键导出交互性的动态结果报告。
4、免疫组库测序经验丰富,助力发表高分SCI文献:
样本类型:
组织、血液、培养的细胞系、制备好的单细胞悬液
注:若客户样本为组织,且无能力进行组织解离来获取单细胞悬液,烈冰将尽可能提供技术及实验上的帮助,但因不同类型样本的特异性,无法保证实验方法适用于所有类型组织。
质量要求:
1. 细胞活性大于70%;
2. 浓度为500-2000细胞/μl;
3. 体积不小于200μl;
4. 细胞培养基及缓冲液不能含Ca2+和Mg2+;
5. 细胞体积小于40μm。






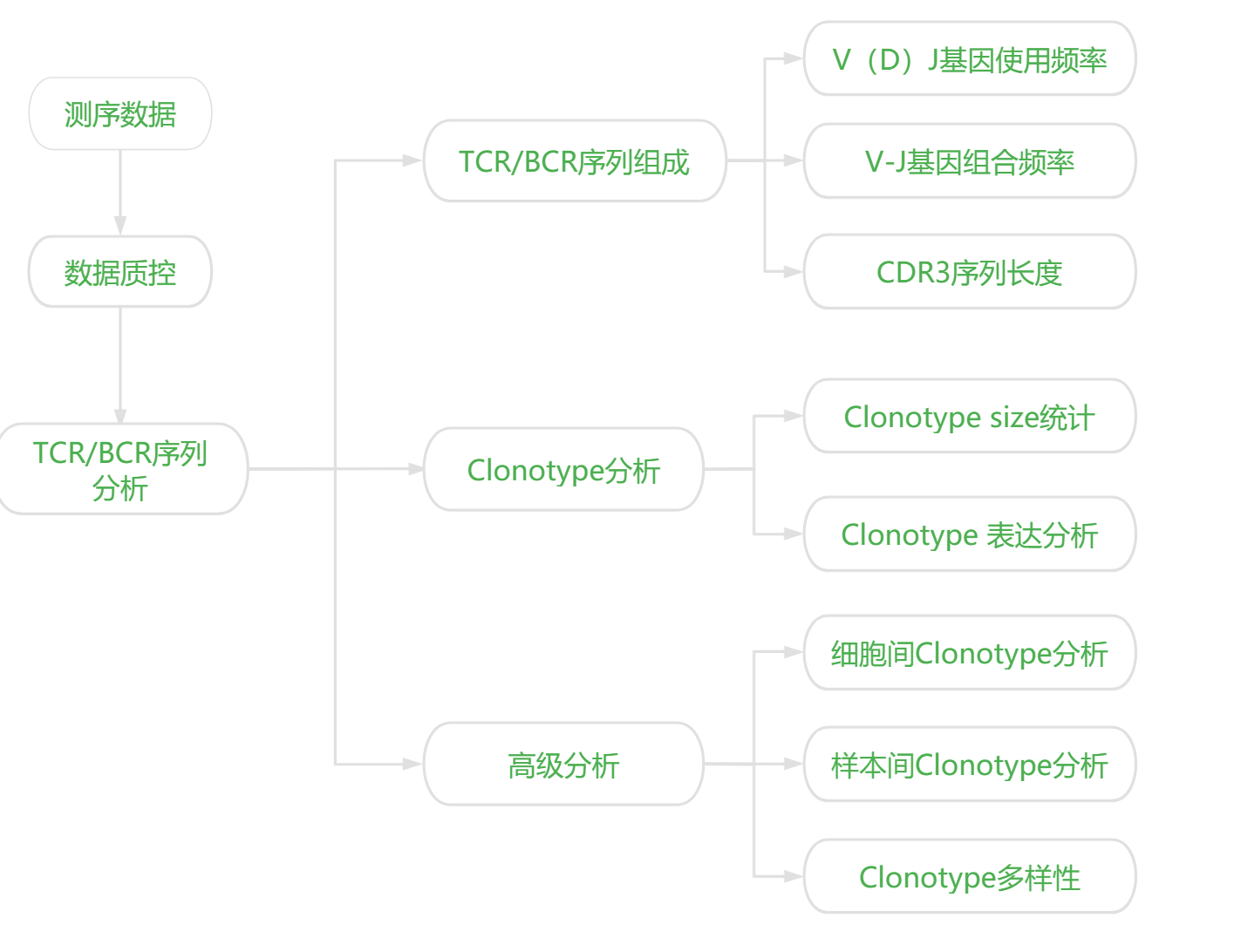
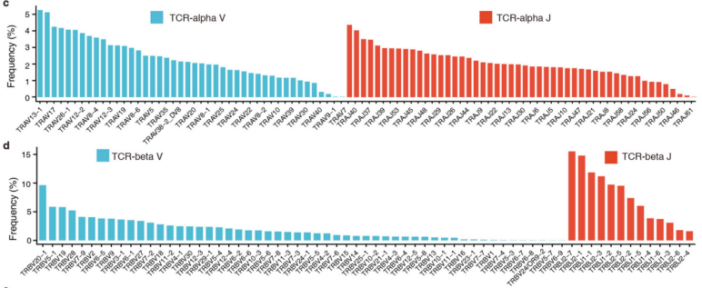
V(D)J基因的使用频率:上图主要展示了TCR序列中V基因的使用情况
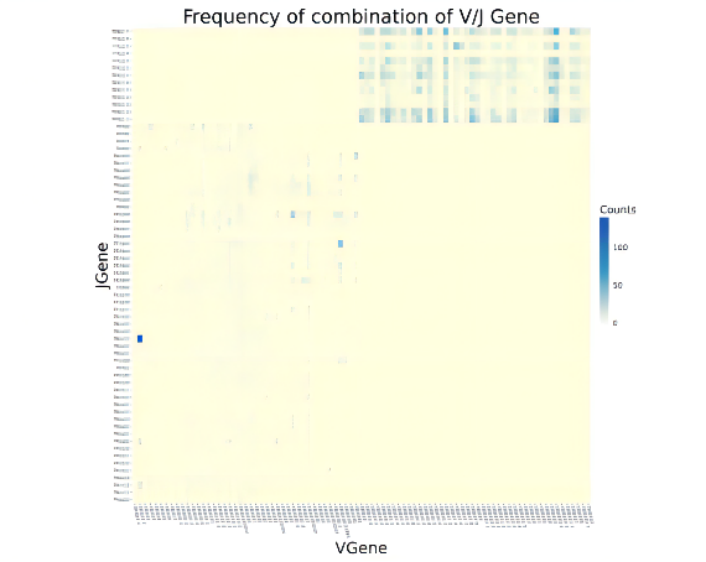
注:横坐标为V基因,纵坐标为J基因
V-J基因组合频率:下图主要展示了TCR序列中V-J基因组合情况。
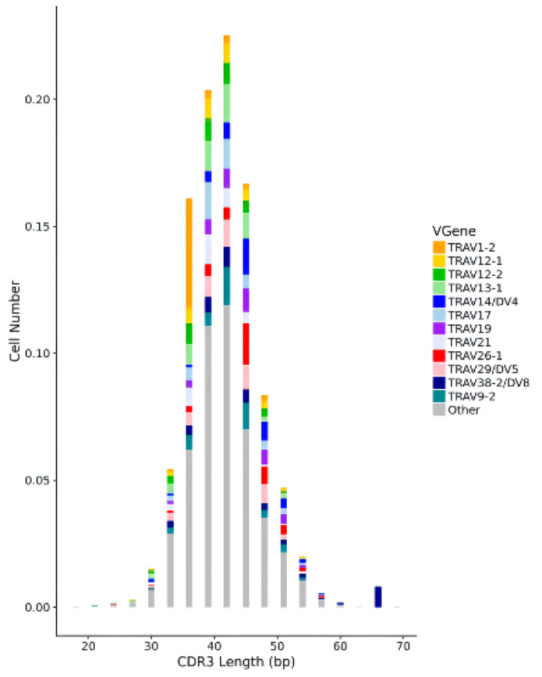
注:横坐标为CDR3长度分布,纵坐标为细胞占比
CDR3序列长度:上图主要展示了CDR3序列的长度分布,以及使用频率最高的12个TRAV基因对应的CDR3长度信息。
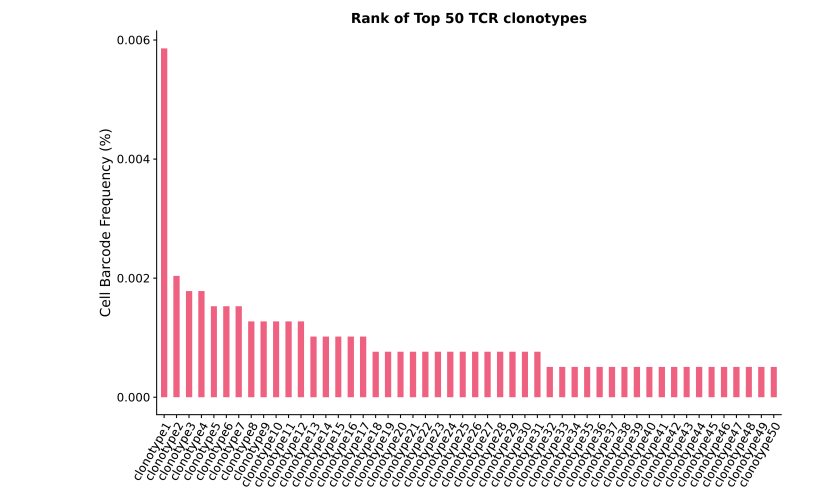
注:横坐标为clonotype编号,纵坐标为细胞占比
克隆频率统计:该图主要展示了TOP50 clonotype对应的细胞占比。
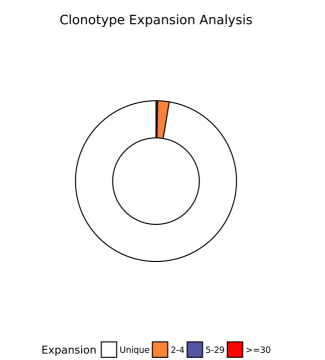
注:Unique或数字: 每个clonotype对应的细胞数(size)
克隆增殖统计:下图主要展示了不同size对应的clonotype的占比情况
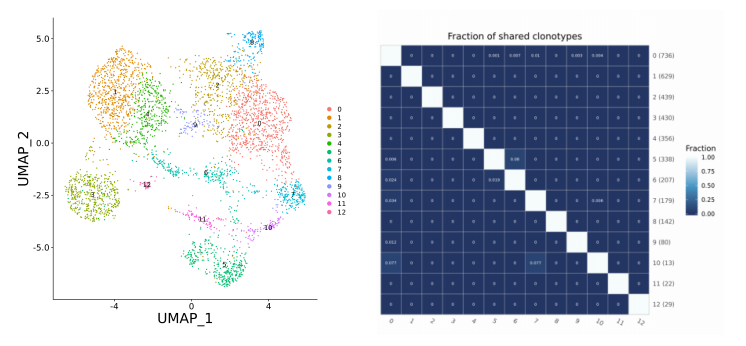
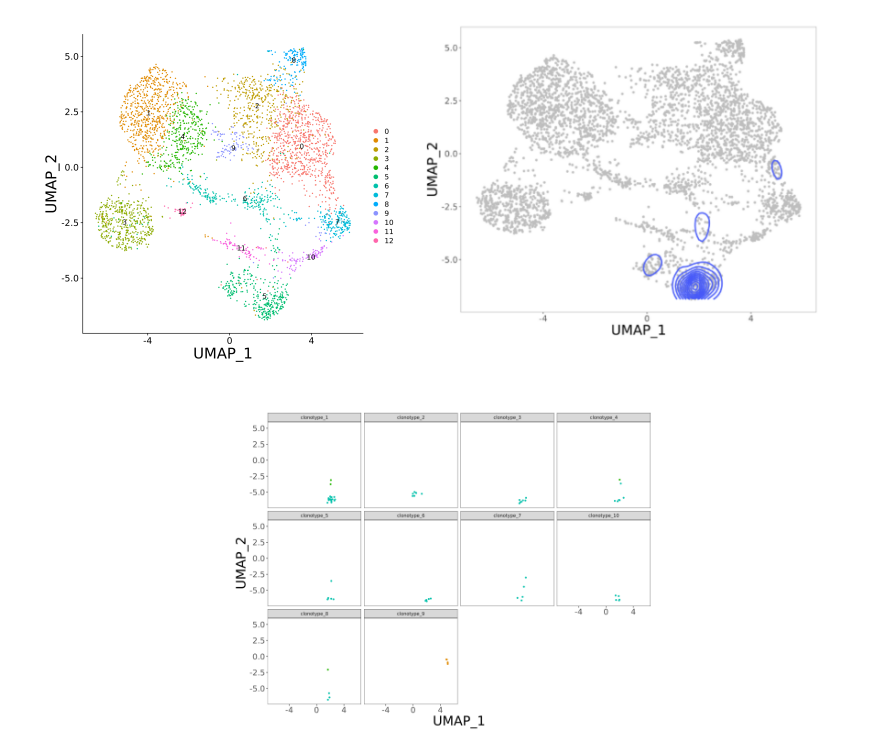
注:右图中,XY轴均为cluster编号,括号内为该cluster中检测到TCR序列的细胞数
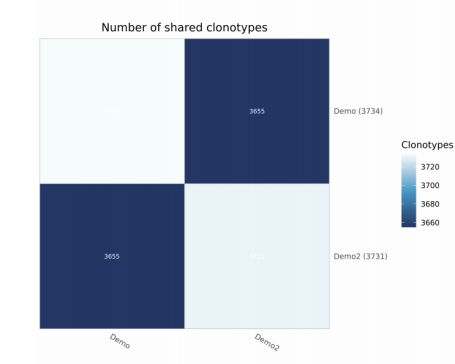
注:横向纵向均为样本名称,括号内为该样本中检测到的clonotype数,色块内为overlap的clonotype数。
[1] MHC class Ib–restricted CD8+ T cells possess strong tumoricidal activities. PNAS.2023 Aug; IF=11.1
[2] Prmt5 deficiency inhibits CD4+ T-cell Klf2/S1pr1 expression and ameliorates EAE disease. Journal of Neuroinflammation. 2023Aug; IF=9.3
[3] Systemic immune dysregulation in severe tuberculosis patients revealed by a single-cell transcriptome atlas. Journal of Infection. 2023Mar; IF=28.2
[4] Tumor-intrinsic YTHDF1 drives immune evasion and resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors via promoting MHC-I degradation. Nature Communications. 2023 Jan; IF=16.6
[5] Single-Cell Landscape Highlights Heterogenous Microenvironment, Novel Immune Reaction Patterns, Potential Biomarkers and Unique Therapeutic Strategies of Cervical Squamous Carcinoma, Human Papillomavirus_x005f Associated (HPVA) and Non-HPVA Adenocarcinoma. Adv Sci. 2023 Jan; IF=15.1
[6] Influenza vaccination features revealed by a single-cell transcriptome atlas. Journal of Medical Virology. 2022 Sep; IF=12.1